The AGC Group’s Sustainability Management
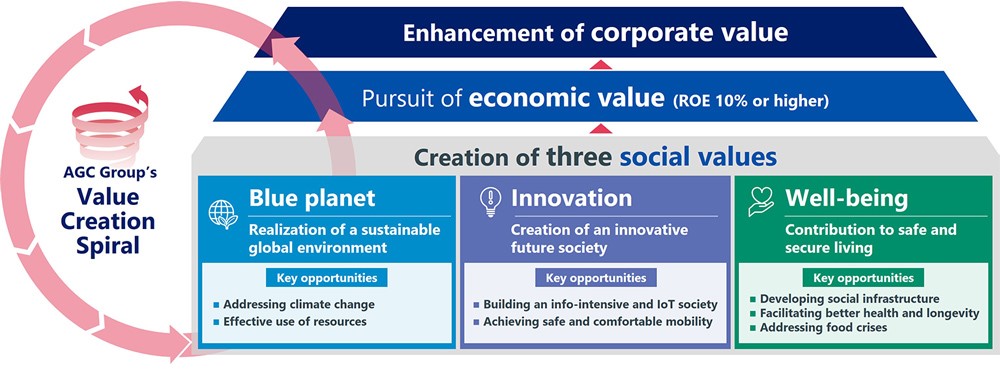
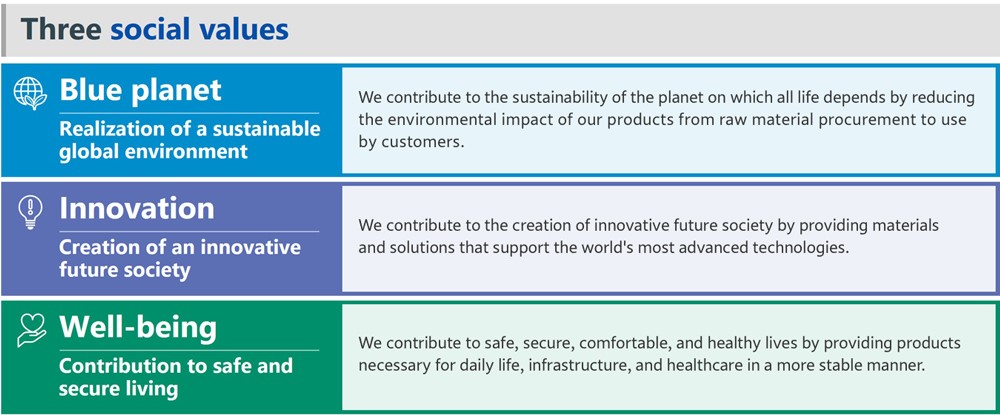
The core approach of the AGC Group's sustainability management is through the creation of three social values: “Blue planet” , “Innovation”, and “Well-being”. The AGC Group has identified “key opportunities” among the opportunities and risks (materiality) that are important for the AGC Group to contribute to solving long-term social issues facing the world and to achieve sustainable growth of the AGC Group. The AGC Group will contribute to the realization of a flourishing society and the planet by transforming these issues into value through the leverage of its strengths in technology and reputation for dependability, which have been cultivated since its foundation.
Long-Term Social Issues (Materiality)
In light of long-term trends in social issues, the AGC Group has identified major opportunities and risks (materiality) associated with simultaneously achieving the sustainable development of the planet and society and the sustainable growth of the Group.
Based on these major opportunities and risks, the AGC Group has established long-term strategy, strategies for each of its businesses, and sustainability (non-financial) targets, and through pursuit of these strategies and targets, aims to create social value and economic value, thereby enhancing corporate value of the AGC Group.
- Key Opportunities
- Key Risks
Addressing climate change
Since the Paris Agreement was reached in 2015, a shift toward decarbonization has been gathering momentum. Stricter energy-related policies and statutory regulations are expected. Also, socially calls are growing for companies to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions.
Effective use of resources
There are concerns that stricter regulations on the use of depletable resources, such as rare earths, and higher demand for water resources accompanying further urbanization could seriously impact the production activities of companies. In addition, as the recycling-based economy accelerates, society increasingly expects companies to reduce waste and promote recycling.
- Key Opportunities
Developing social infrastructure
While the economic growth of emerging countries necessitates the development of such social infrastructure as housing, roads, railroads, and public services, developed countries must deal with the aging of their social infrastructure. oreover, there is a growing need to develop resilient infrastructure that can withstand the intensified disasters being caused by climate change.
Achieving safe, comfortable mobility
The spread of automobiles in emerging countries is causing concern over rising traffic accident deaths. Meanwhile, ddressing the mobility needs of the elderly, those living in less-populated areas, and other vulnerable groups in society is becoming increasingly important. Further, as autonomous driving becomes more widespread, expectations are increasing with respect to the establishment of safety technologies, such as sensors and cameras, and the enhancement of in-car entertainment.
Addressing food crises
The problems of hunger and malnutrition in the world’s poorest regions have yet to be resolved, and there are concerns that the situation will worsen due to disasters and droughts caused by the climate change of recent years. Also, to cope with a growing world population, food productivity must improve.
Building an info-oriented, IoT society
With the spread of information and communication technologies in emerging countries, reliable, inexpensive access to information needs to be provided. In developed countries, the early dissemination of next-generation high-speed communication technologies, such as 5G, promises to improve the quality of remote medical care and information transmission.
Facilitating better health and longevity
Given that the number of young people losing their lives due to non-communicable diseases remains high worldwide, there is a need to reduce such deaths by providing stable supplies of pharmaceuticals for prevention and treatment. In addition, a trend toward increased division and specialization in the pharmaceutical industry, which is aimed at improving the productivity of the industry as a whole and diversifying its risks, is becoming more pronounced.
- Key Risks
Creating socially and environmental-conscious supply chains
As supply chains become more globalized and complex, the risk of issues arising in relation to illegal employment, such as forced labor and child labor, at suppliers and subcontractors is increasing. Further, tighter environmental regulations are leading to concern over potential regulatory violations at operating bases.
Ensuring fair and equal employment and workplace safety
There is a growing need for compliance in employment and respect for workers’ rights as well as for safety measures at manufacturing sites due to the increasing number of unskilled and elderly workers.
Considering relationships with local communities and the environment
Due to population growth and urbanization in various parts of the world, interest in expanding living areas and maintaining biodiversity in surrounding areas is growing. Also, in emerging countries there is an increasing focus on improving quality of life as living standards improve. Efforts to build good relationships with local residents and governments in the vicinity of operating bases are also becoming more important.
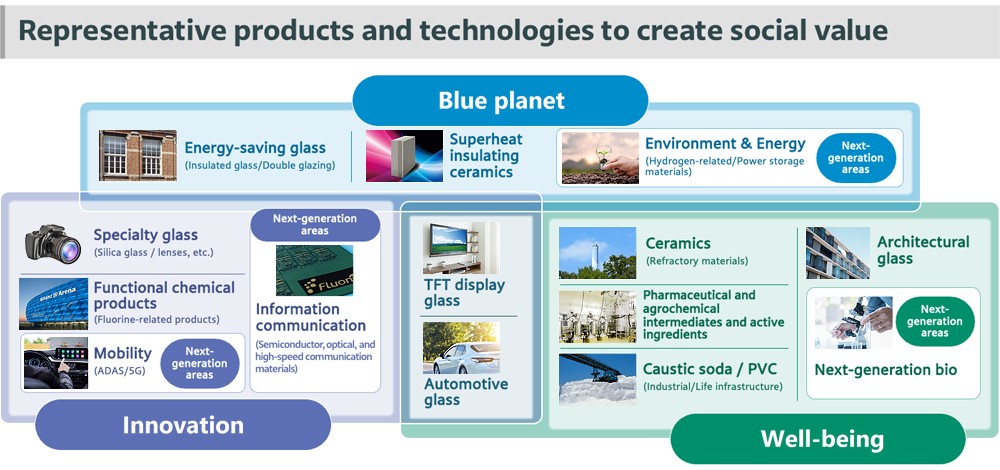
Three Types of Social Value the AGC Group Wants to Create
To date, the AGC Group has expanded its business and created social value by contributing to the development of society and industry. We will continue to create social value by providing materials and solutions.