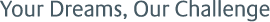What are PFAS?
“PFAS” (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) are a group of chemical substances with a specific chemical structure that contain fluorine atoms. PFAS have many specific characteristics which in combination cannot be effectively replicated by other materials. These characteristics include heat resistance, fire resistance and electrical insulation, which makes them critical in the various aspects of daily life to improve society and support a sustainable, carbon neutral world.
Types of PFAS
There is an extremely large variety of types of PFAS, each with their own different properties2. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), there are approximately 12,000 types of PFAS3. PFOS, PFOA and PFHxS have been banned from production and use in Japan4. These three types of PFAS were listed for restriction under the “Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants” (POPs Convention), because PFOS, PFOA, and PFHxS have been found to be persistent in nature or bioaccumulative, and may have potential adverse health effects. The term “PFAS contamination” is found in some media reports in Japan, but more precisely, this refers to contamination by these three restricted types of PFAS.